Good morning, Beirut! Check out this video to see Bus Map Project co-founder Chadi Faraj speaking with MTV Lebanon about our initiative!
Tag: Policy
Taking the Bus to Movenpick: First Meeting of the INDC Working Group in Lebanon

Today’s First Meeting of the INDC Working Group that is following up on Lebanon’s COP21 climate action targets was very informative. It was good to hear updates from Dr Ziad Nakat on the World Bank-led Greater Beirut Urban Transport Project that we keep reading about in the news. From today’s presentation, the project seems to combine the MoPWT-DGLMT’s ‘Pilot Project’ for a comprehensive bus network in Beirut with three BRT ‘backbones’ on the northern, southern and eastern axes.
We would have liked to hear more about how this project will fit into the existing transit system. Indeed, there’s a lot left unsaid when the project is referred to as “the first public transport system in Lebanon” while also saying that there are “important challenges related primarily to arrangements with existing public transport operators.”
We appreciated learning about the EU-funded SISSAF Project, and their work with the MoPWT to develop a Land Transport Strategy. Again, it wasn’t clear how this fits into existing projects, including the GBUTP, but the comprehensiveness of the project was impressive.
It was interesting to learn from First Climate Consulting about plans to implement a car scrappage and replacement program next year, focusing on ‘red plate’ vehicles in the first phase. Hopefully, this project will also take into consideration why transit operators keep their vehicular maintenance costs down, and, indeed, why so many — especially retirement-age men — buy or rent red plates and start driving taxis in the first place.
Our favorite takeaway from the event? By a show of hands, it seemed that we were the only two attendees who took the bus to the conference. Climate action starts today, no?
Interview: BMP in The Daily Star
The system is remarkably self-sustainable, even though it is almost entirely unregulated.
We loved sharing our bottom-up, incremental vision of infrastructural activism with The Daily Star!
What do you think? Are we “hiding behind our fingers” as one commenter claims?
“Under The Bridge” by Nora Niasari
We’re excited to share this documentary by our friend Nora Niasari, now available to view online! Production of this short film on Beirut’s public transport began in 2010. In 2011, “Beirut, Under the Bridge” was awarded ‘Best Director Documentary’ and ‘Special Jury Prize Documentary’ at the 11th Beirut International Film Festival, and was broadcast on CNN and MTV Lebanon.
We asked Nora to reflect on her project, nearly six years on: “For me, Beirut is a city of unspoken potential. In 2010, our film stirred up a mostly dormant debate about public transport, asking why the sector was effectively buried alive after the civil war. We learned many things, but today, transport workers and transport users alike are still asking, “Where are we headed?”
Read more about Nora’s experience here.
The Traffic Crisis
Citizen Consultation Lebanon is an interesting initiative addressing civic rights and needs from a grassroots perspective, including the right to public transport, as seen in this legal briefing. Have a look to learn more about the root causes of the traffic crisis we are facing today, and make sure you also check out Legal Agenda’s earlier briefing (in Arabic).
At the same time, we would like to point out how little attention the existing transit network is given in such documents. This is a common issue; most people working on transport/transit in Lebanon have a very good idea about everything the state has failed to do, or has done badly, but the elephant in the room — the complex networks of people and places filling the gap left open by state neglect and mismanagement — is consistently ignored, downplayed, or put to one side.
We believe that the existing transit system is more than just a lack (“UNregulated,” “UNorganised,” “INefficient,” etc), a mistake, or an empty placeholder for something yet to come. It’s also more than a de facto reality we must contend with in order to promote change — it is a network of citizens just like us. Time to start talking.
Bus Map Project at #CitizenDesigner
This week, we took part in #CitizenDesigner, a three-day event hosted by Graphicism at the Lebanese University in Hadath. Here’s a quick summary of what we presented:
It’s important to emphasize that we’re not proposing anything radically new. We draw inspiration from nearby experiences like the Nairobi Digital Matatus initiative, and the World Bank’s mapping project in Egypt. We can learn from these examples, and adapt them to our own context.
While the idea and technology might not be new, our approach to public transport advocacy in Beirut is a little bit different. Bus Map Project aims to be collaborative, open source, gradual and modular. All these buzzwords simply mean that we are a platform for your input and concerns. They also mean that we believe in treating the existing bus system the same way. Ya3ne, for us, “Citizen Design” means taking existing systems seriously.
Bus Map Project at Green Line’s Transport Conference

Thank you Green Line for inviting us to discuss our tiny project at yesterday’s “Local Governance of the Transport Sector: Roles & Responsibilities” event. It was great having such a wide range of actors and stakeholders in the same room, and we hope to see this pluralism strengthened and expanded in the future.
As was clear from the rich debates we heard throughout the day, different perspectives will not always see eye to eye. What we think about transportation is determined by what we believe about government, economy, society, etc. We all know that. But even if we agree on the broad slogans, the difficult questions of strategy, method and approach will remain.
As Bus Map Project, we spoke from the perspective of bus riders. While we do not claim to represent anyone other than ourselves, our thinking — as summarized in this slide — is founded on a simple belief: public transport can improve when the riding public begins to speak as riders. This can happen in so many ways: when ridership expands, or when the sector enters the public eye like electricity or waste management has done, or through the relationships we form in the process of collective mapping, etc. But at its most basic level, this begins in the simple act of insisting that *we exist* . . .
That is the core message of our project. The map is a tool we put to use.
Statement of Solidarity with Ongoing Protests in Beirut | #Aug29
On August 22, a campaign based around the ongoing waste (mis)management crisis in Lebanon became much much more. The movement called طلعت ريحتكم struck a chord with people across Lebanon, and brought thousands into Riad al-Solh Square to voice their anger over a wide range of policy failures and socioeconomic issues. At the center of this discontent is the generalized syndrome of deadlock in governance in the country, but others have gone further in their diagnoses. Many have focused on the endemic culture of nepotism and corruption among the semi-feudal political class ruling the country. Others have struck at the root, focusing on the confessional system itself as the perpetual engine of division, unaccountability and immobilism. Others have dug even deeper into the capitalist system as the context of contexts for our problems.
In the days that followed that fateful Saturday, several factors have pushed and pulled the movement in different directions. First, there was the inexplicable and inexcusable state violence against protesters, which fueled anger and encouraged more people to join. Second, there were the fears of party-orchestrated infiltration and sabotage, and the resulting controversy among movement supporters over the classist and sectarian overtones of these fears, and the ways that protest organizers chose to respond to them. Finally, there was the plurality of proposals and counterproposals for the way forward with movement demands, stemming from the various criss-crossing analyses described above. By August 29, the movement grew far beyond its initial scope and framing as #YouStink, and became a true platform for mass political action.
Today, a host of inspiring groups, new and established, are active “in the square” — community-based campaigns like عكار_مش_مزبلة, citizen journalism projects like أخبار الساحة, recycling initiatives like Sar Lezem Rassak Yifroz, anti-capitalist fora like المنشور, student organizations like AUB Secular Club, and advocacy networks like National Campaign for Sustainable Transportation, etc.
This means that the visions, missions and approaches are now many. Where do we go from here?
Bus Map Project was conceived as a modest, small-scale intervention in the gaps between state neglect and policy-oriented advocacy. We chose a pragmatic approach that strategically set aside the twin issues of rights and demands. We stubbornly focused on the present — on the bus system as it exists today, without quick judgement or dismissal — because we felt that other pro-transit campaigns have either focused too much on the past (e.g. the state’s neglect of public transport) or too much on the future (e.g. a desired public transport system). More fundamentally, we chose an approach that would bypass the state altogether — with or without a president, with or without a parliament, with or without a responsive Ministry of Public Works & Transport, we want to begin collectively building our own tools that help us make sense of and navigate our cities.
We support the current climate of protest. We believe that more awareness of the systemic problems that produce so many failures across so many sectors — from housing to transport to the environment — is important. Our project has only just started, but we wish to contribute to this ongoing conversation sparked by #YouStink by calling for more small-scale, closely-allied, locally-based, and non-state reliant projects focused on the tail-end of the crises created by Lebanon’s broken system of governance. The movement’s broader slogans — anti-corruption, secularism, electoral reform, parliamentary renewal — are of vital importance, but we believe that Lebanon also needs solutions in the here-and-now. We need better representation, better institutions, etc, but we also need less dependence, less centralization, less delegation of our power to connect and work together as civic actors.
This is not a call to “de-politicize” the movement — that is impossible. It is, however, a plea for more fidelity to the immediate, to the concrete, and to ourselves. There is strength in numbers — a single-issue campaign acting alone will struggle to accomplish anything, but a sustained and focused project acting within a broad network of supportive campaigns is more likely to succeed, for the benefit of all. Yalla.
If you are interested in learning more about how you can help Bus Map Project, please do not hesitate to contact us.
The Nightmare of Transit Deserts
‘These are the stories of citizens who head to Beirut and its environs for work, every day, from the four corners of the nation, and who return to their home towns and villages in the evening to ‘divide the bread’ of their workday with their families.’
Have a look at this very important article (in Arabic) that first ran in As-Safir Newspaper. The issue of public transport cannot be disconnected from the prohibitive price of rent and housing in Beirut, the over-concentration of jobs in urban centers, and other wider issues of demography.
Areas served by few or infrequent buses — called ‘transit deserts’ — reflect these socioeconomic patterns, and can often make them worse by skewing our choices of where to live and work. The lack of night services on many routes also affects people’s choices of where to go and who to interact with.
Mapping can help us figure out which regions are under-served by public transport, and in doing so, point to underlying inequalities that can be improved — but not solved — by better network coverage.
How are your day-to-day choices of where to live, who to meet, etc., affected by the transport system? Let us know on our Facebook page.
So, Does Public Transport Really Exist?
The following is adapted from a post by Bus Map Project co-founder Jad Baaklini, first published on his personal blog. It features research material produced by ODDD in the Maten.
For a country that’s turned the word ‘philosophize’ into an insult (bala falsafeh ya zalameh), we sure do drift into weird ontologies, without even trying. What’s the difference between existing and not really existing? Can something actually exist but not really really exist?
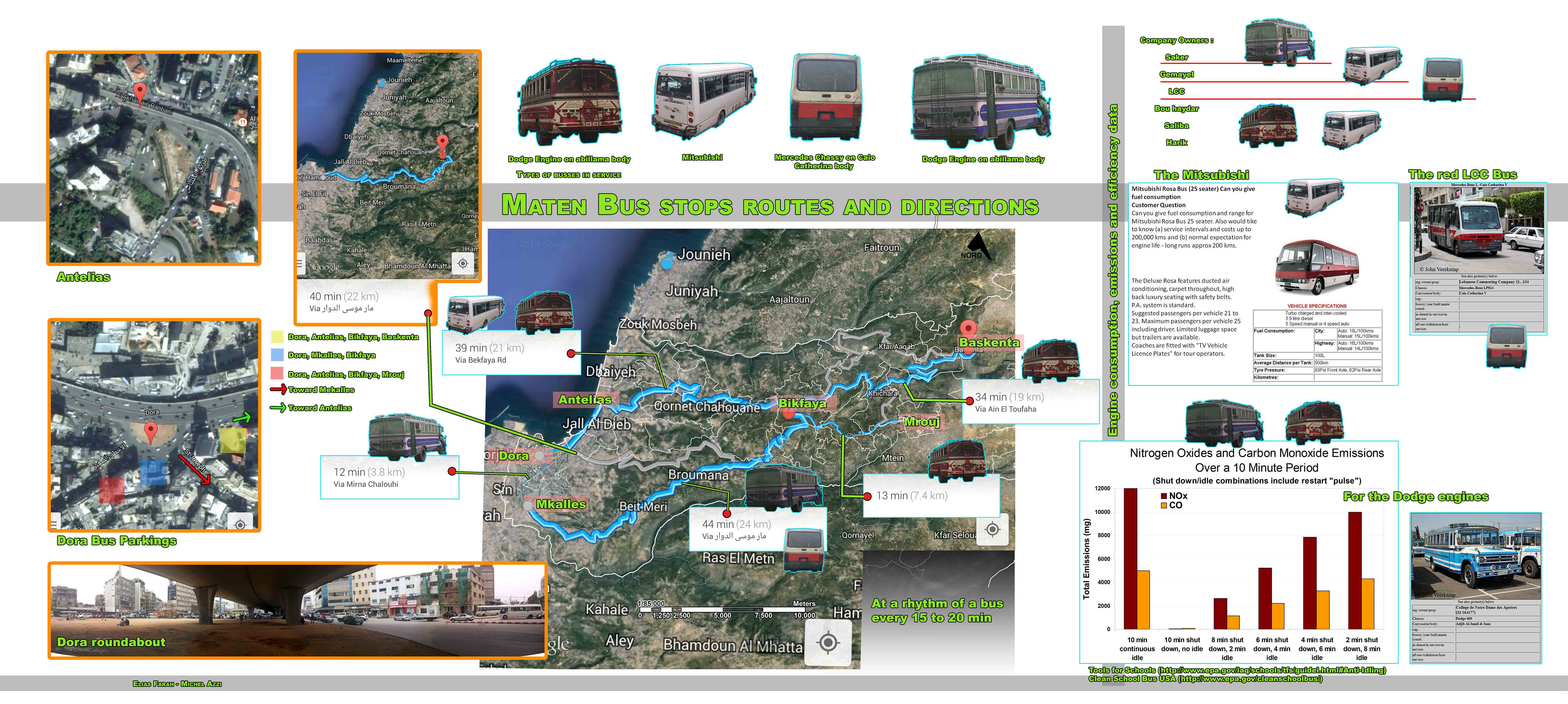
I mean, clearly something that looks like public transport exists. Mitsubishi Rosa, Nissan Civilian, Fargo/Abi Lama — these are actual vehicles that very real people board every day to actually get from point A to point B. They have particular owners and particular drivers, who are associated with specific license plates and driving permits.
They gather in specific locations, which are part of complex and precise territorial arrangements that keep the tenuous peace between different fleets and route associations in this highly-competitive market. Fuel is consumed, money is made, and the public is transported from place to place. How can something so complicated be so easily dismissed?

For many people, the interactions and exchanges that make up this system are invisible or obscured. They may see a bus pass by from time to time, but they can’t tell if its a private shuttle or a school bus, or where it might be heading. So when these people say that public transport doesn’t exist in Lebanon, they do so out of a lack of familiarity with how all these seemingly chaotic parts — this clustering around Cola, that bus making this cab driver curse, etc — fit together. This is understandable. If you’ve never heard of Beirut, would you consider moving there? The same goes for Beirut’s bus system: if you don’t know that 1000 LL (less that $1) can take you all the way from Hamra to Ain Saadeh via Bourj Hammoud — a distance of more than 15 kilometers — you could not possibly begin to consider alternatives to driving there yourself (if you have a car) or paying up to twenty times as much for a taxi.
The problem of unfamiliarity is made more difficult by the fact that there are few tools or resources available to help potential bus passengers learn about these routes. Even when maps are made — and here is one attempt by Bus Map Project co-founder Chadi Faraj — there is still almost no dedicated road infrastructure to help you figure out where to catch these buses, on street level. It’s just something that — at the moment — you have to learn through trial and error, or by asking regular bus riders.

Learning to navigate a city this way can be a little bit intimidating at first. Everything seems random, but once you start paying attention, you’ll very quickly see that these bus networks have many regularities and routines: you don’t have to constantly guess where the Number 5/8 bus passes through Mar Mkhael on its way from Hamra to Ain Saadeh, for example — it’s always the same place: Badawi Street. The bus then turns the corner onto Armenia Street, usually stopping at the traffic lights, before then heading over the Nahr Beirut bridge into Bourj Hammoud. There’s no visible ‘bus stop’ anywhere along this route, but the bus will stop for you if you’re waiting for it.

Of course, not everyone is being literal when they say that public transport doesn’t actually exist. For these people, everything I just wrote is exactly why they believe that it doesn’t really exist — emphasis on “really.” This is because, according to their definition of public transport, what I described does not qualify. To them, a system that you have to “figure out” is no system at all, especially when its made up of a hodgepodge of gaudy bostas and second-hand minibuses imported from who-knows-where. To these detractors, what we have in Beirut is not “real” public transport for two simple and interrelated reasons: 1) “real” public transport must be publicly-owned (wen el dawleh?), and 2) “real” public transport must look, feel and behave a certain way (mrattab, eben 3ayleh, etc).
Or, as one activist I spoke to put it:

Let’s address these issues step by step. First of all, while state-owned bus routes do exist — that blue ticket above is from one of them — they certainly have their limitations. First, OCFTC bus fleets are very small, so trying to see one on the road can feel like being on safari. Second, their routes and designations overlap but don’t match with those of the larger and more popular, privately-owned fleets. So a Number 5 OCFTC does not go the same place as the Number 5/8 I described above, even though you can see both on the Jdeideh-Fanar-Ain Saadeh section of that route (and let’s not start comparing these numbers to those of vans). More harmonization between the state- and privately-owned bus networks would obviously be much more helpful for all of us, but I wouldn’t hold my breath waiting.
The question of what the government should be doing in this sector is, of course, very important, but it’s also very complex. Should the state buy new buses, or should it focus on providing road infrastructure? Should it try to compete with the privately-owned bus networks, or should it play the role of overall regulator? Can it help negotiate between competing fleets? If it runs its own buses, which gaps in the network should it fill? What passenger needs should it target? All of these are important questions that are sadly not on the table right now. But the fact that the state has neglected the public transport sector does not mean that those who are currently filling its service voids are illegitimate, or unimportant. Any lobbying of government that does not take into account the system that developed in its absence is doomed to failure. I would also call it unethical, even if, right now, it sometimes looks like the privately-owned system has no real interest in seeing the public sector revived. As Aoun (2011) argues in a paper she gave at the Transportation Research Board 90th Annual Meeting, a major obstacle to any meaningful change happening in the sector is “the uncertainty that [existing] transit operators face” (p. 8). Aoun writes:
“Although [operators] prefer more regulation and order under transit reform on one hand, they are also apprehensive of their future roles, on the other hand. Placing blame on each other also suggests a “prisoners dilemma” scenario in which each stakeholder operates individualistically, lacking the reassurance to cooperate in a mutually beneficial system.” (2011: 8)
If we’re serious about breaking out of this scenario, we need to urge the state (and pro-transit activists) to avoid stoking these feelings of apprehension and mistrust by dismissing the existing transit system wholesale.
This leaves us with the issue of how public transport should look, feel and behave. Some people will admit that some kind of bus system exists in Lebanon, but will then rush to add: but it’s filthy and unreliable. For these people, public transport will only really exist when it starts to look like an image they have of Paris, London or NYC — images that are transformed in their minds and rhetoric into simplistic approximations of imagined machine-like efficiency that doesn’t really match the way transit actually functions in those cities.
I don’t want to challenge these beliefs, and I certainly don’t want to romanticize the bus. There is certainly much room for improvement in the sector, most notably in the area of accessibility, as all buses currently available are not designed to accommodate wheelchair users, and pose a unique challenge to elderly passengers. While people who say that there are “no schedules” are exaggerating, the timeliness of buses can always be improved. But as a twitter friend once put it eloquently, the main question for people who want to see the system improved is: how can we dramatize the need for change without scaring people off from even trying what already exists? Do we have to dismiss the whole system to make a point?
My response to those who say they’d love to ride public transport if only public transport existed in Lebanon is this: it does, wallah, it does — now go try it, and see if you can find a way to integrate it into your life.
